POP3 vs IMAP: Definitions
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) and IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) are both protocols used for retrieving email from a server, but they have some key differences:
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3)
Definition: POP3 is a protocol used to download emails from a server to a local device. Once the emails are downloaded, they are typically deleted from the server, though some configurations can keep a copy on the server.
Key Features:
- Download and Delete: Emails are downloaded from the server to the local device and are usually removed from the server.
- Offline Access: Once downloaded, emails are stored locally and can be accessed offline.
- Single Device Usage: POP3 is often used when accessing email from a single device since it doesn’t sync emails across multiple devices.
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol)
Definition: IMAP is a protocol used to access and manage emails stored on a remote server. Emails remain on the server and can be accessed from multiple devices.
Key Features:
- Server-Side Storage: Emails are stored on the server, which means you can access your email from multiple devices and have a consistent view.
- Synchronization: Changes (such as read/unread status, folders) are synchronized across all devices accessing the account.
- Online and Offline Access: While you can access and manage emails online, IMAP allows for offline access to emails that have been previously synced.
Table of Contents
What are the differences between POP3 and IMAP?
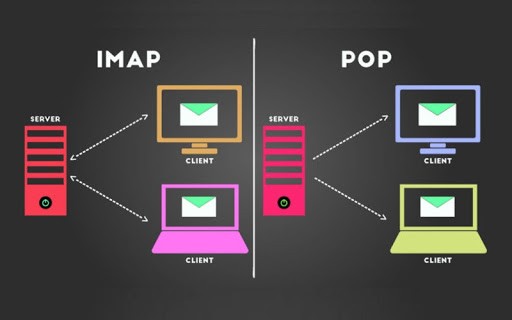
POP3 vs IMAP are both email retrieval protocols, but they differ in several key aspects, including how they handle email storage, synchronization, and accessibility. Here are the main differences:
Email Storage
- POP3:
- Downloads emails from the server to the local device.
- Emails are typically deleted from the server after being downloaded (though this behavior can be changed).
- Local storage means emails are accessible offline after being downloaded.
- IMAP:
- Emails remain on the server.
- Emails are accessed and managed directly on the server.
- Emails can be accessed from multiple devices, maintaining synchronization across all devices.
Synchronization
- POP3:
- Does not support synchronization across multiple devices.
- Each device downloads its own copy of the emails, leading to possible inconsistencies.
- Actions (such as marking an email as read) are not reflected across other devices.
- IMAP:
- Supports full synchronization across multiple devices.
- Any action taken on one device (reading, deleting, moving emails) is reflected on all other devices.
- Provides a consistent view of emails across all devices.
POP3 vs IMAP Accessibility
- POP3:
- Primarily designed for use on a single device.
- Emails are downloaded and stored locally, making them accessible offline.
- Not ideal for users who need to access emails from different devices.
- IMAP:
- Ideal for accessing emails from multiple devices.
- Emails are stored on the server and can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Allows for offline access to emails that have been previously synced.
POP3 vs IMAP Email Management
- POP3:
- Limited to basic email management (download, delete).
- Folders and labels created locally are not synchronized with the server or other devices.
- Suitable for users who prefer to manage emails locally.
- IMAP:
- Supports advanced email management (folders, labels, searching).
- Folder structure and organization are synchronized across all devices.
- Ideal for users who require robust email management and organization.
Bandwidth Usage
- POP3:
- Generally uses less bandwidth as emails are downloaded once and stored locally.
- Suitable for users with limited internet access.
- IMAP:
- May use more bandwidth due to constant synchronization with the server.
- Each action (reading, moving emails) requires communication with the server.
Use Cases
- POP3:
- Best for users who access their email from a single device.
- Suitable for users with limited or intermittent internet access.
- Ideal for those who prefer to keep their emails stored locally.
- IMAP:
- Best for users who need to access their email from multiple devices.
- Suitable for users who need consistent email synchronization across different platforms.
- Ideal for those who require advanced email management features.
In summary, the choice between POP3 and IMAP depends on your specific needs for email access, synchronization, and management. POP3 is simpler and uses less bandwidth, while IMAP offers more flexibility and better support for multiple devices and complex email organization.