What is Bandwidth

Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transmitted over an internet connection in a given amount of time. It is typically measured in bits per second (bps) and its multiples, such as kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps).
Table of Contents
Key Points About Bandwidth:
- Capacity: Bandwidth represents the capacity of a network connection to transfer data. Higher bandwidth allows more data to be transmitted in a shorter period of time.
- Usage: In the context of web hosting, bandwidth refers to the total data transfer to and from your website, including visits, downloads, uploads, and other data exchanges.
- Importance: Adequate bandwidth is crucial for ensuring that websites load quickly and can handle multiple users simultaneously without performance issues.
- Monitoring: Web hosting services often provide tools to monitor bandwidth usage to prevent overage charges and ensure optimal performance.
Practical Example
- Website Traffic: When visitors access your website, data is transferred between the server and their devices. This data transfer consumes bandwidth.
- Downloads/Uploads: Files downloaded from or uploaded to your website also consume bandwidth.
Understanding and managing bandwidth is essential to ensure your website runs smoothly and efficiently, especially during traffic spikes or heavy data usage periods.
How to Check Bandwidth Usage In cPanel
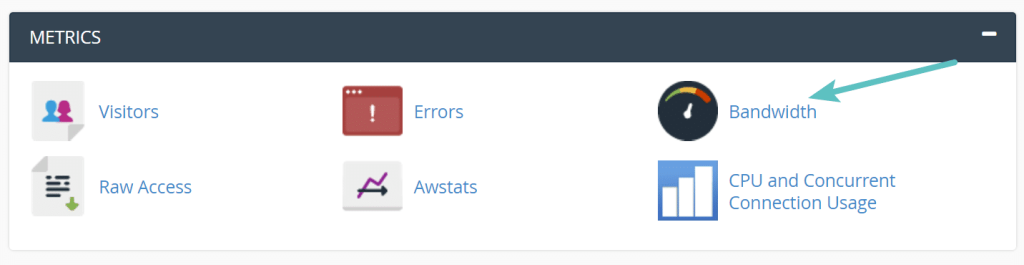
To check bandwidth usage in cPanel, follow these steps:
- Log in to cPanel:
- Open your web browser and go to your cPanel login page.
- Enter your username and password to log in.
- Navigate to the Metrics section:
- Once logged in, scroll down to the “Metrics” section.
- Click on Bandwidth:
- In the “Metrics” section, click on “Bandwidth.”
- View Bandwidth Usage:
- The Bandwidth page will show a detailed overview of your bandwidth usage. This includes:
- Current month’s bandwidth usage.
- Bandwidth usage for the past 24 hours, the past week, and the past year.
- The usage is usually broken down by HTTP (web traffic), IMAP/POP3/SMTP (email traffic), and FTP (file transfer traffic).
- The Bandwidth page will show a detailed overview of your bandwidth usage. This includes:
This information helps you monitor how much bandwidth your website is using, allowing you to manage and optimize your resources effectively.
What are the Advantage and Disadvantages of Bandwidth
Bandwidth, the amount of data that can be transmitted over an internet connection in a given amount of time, is a critical aspect of networking and internet usage. Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of bandwidth:
Advantages of Bandwidth
- Improved Performance:
- Faster Data Transfer: Higher bandwidth allows for quicker downloading and uploading of files, leading to more efficient work processes.
- Better Streaming Quality: High bandwidth enables smoother streaming of high-definition videos without buffering.
- Enhanced Online Gaming: Provides a better gaming experience with lower latency and reduced lag.
- Supports Multiple Devices:
- Concurrent Usage: High bandwidth can support multiple devices connected to the network simultaneously without significant drops in performance.
- Smart Homes: Essential for smart home systems where various devices (e.g., security cameras, smart TVs, home assistants) are connected.
- Business Efficiency:
- Remote Work: Facilitates remote work by allowing seamless video conferencing and real-time collaboration on cloud-based platforms.
- Cloud Services: Supports the use of cloud storage and applications, making business operations more flexible and scalable.
- Future-Proofing:
- Scalability: High bandwidth can accommodate future growth and the increasing data needs of applications and devices.
- Technological Advancements: Prepares networks for new technologies and higher data demands.
Disadvantages of Bandwidth

- Cost:
- Higher Expenses: Higher bandwidth typically comes with increased costs, which can be significant for both individuals and businesses.
- Infrastructure Investment: Upgrading infrastructure to support higher bandwidth can be expensive.
- Potential for Overuse:
- Data Caps: Some ISPs impose data caps, and exceeding these limits can result in additional charges or reduced speeds.
- Network Congestion: In shared environments, high bandwidth usage by one user can negatively impact others.
- Security Concerns:
- Increased Attack Surface: Higher bandwidth can attract more sophisticated cyber attacks, requiring robust security measures.
- Data Privacy: With more data being transmitted, there is a greater risk of sensitive information being intercepted if not properly secured.
- Environmental Impact:
- Energy Consumption: Higher bandwidth networks can consume more energy, contributing to a larger carbon footprint.
- Electronic Waste: Frequent upgrades to network hardware can lead to increased electronic waste.