What is a Static Website?
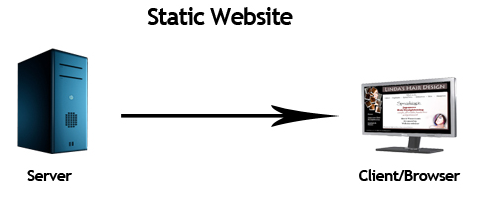
A static website is a type of website that is composed of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, and other web resources, where the content is fixed and doesn’t change dynamically. In other words, the content remains the same for every user who visits the site. These websites are typically built using tools like HTML, CSS preprocessors (such as Sass or Less), and front-end frameworks (like Bootstrap or Foundation). Since there’s no server-side processing involved, the websites are often simpler to host and can offer faster loading times compared to dynamic websites.
Table of Contents
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of static website ?

Advantages:
- Simplicity: Static websites are generally easier to develop, deploy, and maintain compared to dynamic websites because they don’t require server-side processing or databases.
- Speed: Since static websites consist of pre-built HTML files, they typically load faster than dynamic websites, leading to a better user experience.
- Security: Static websites are less prone to security vulnerabilities because there’s no server-side scripting or database interactions, reducing the potential attack surface.
- Cost-effectiveness: Hosting for the websites is often cheaper since they don’t require server-side resources like databases or application servers.
- Scalability: The websites can handle high traffic volumes mor
- e easily because they are served directly from a web server without any server-side processing.
Disadvantages:
- Limited functionality: Static websites are suitable for simple content delivery but may lack advanced features like user interactivity, personalized content, or real-time updates.
- Maintenance challenges: Updating content on the websites may require manual editing of HTML files, which can be time-consuming and error-prone, especially for large sites.
- Complexity for large sites: Managing a large number of the pages can become cumbersome without proper organization and automation tools.
- Interactivity limitations: Since the websites don’t have server-side processing capabilities, implementing features like user authentication, form submissions, or dynamic content generation can be challenging.
- SEO limitations: While static websites can be optimized for search engines, they may face limitations in dynamic content generation and personalized SEO strategies compared to dynamic websites.
What is a dynamic website?
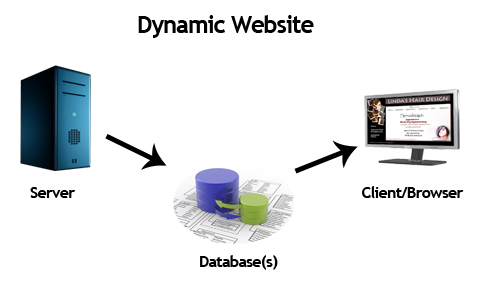
A dynamic website is a type of website that generates content on the fly in response to user interactions or requests. Unlike static websites, where the content remains the same for all users, dynamic websites can personalize content, interact with databases, and respond to user inputs in real-time.
What are the advantages and disadvantages for dynamic website?

Advantages:
- Interactivity: Dynamic websites can provide a more engaging user experience by offering interactive features such as forms, user-generated content, comments, real-time updates, and personalized recommendations.
- Customization: Dynamic websites allow for highly customized and personalized content based on user preferences, behavior, or demographics, enhancing user engagement and satisfaction.
- Content Management: Dynamic websites often incorporate content management systems (CMS) that make it easier to add, edit, and organize content without directly manipulating HTML files, facilitating efficient website maintenance.
- Database Integration: Dynamic websites can interact with databases to store, retrieve, and manipulate data, enabling functionalities like user authentication, e-commerce transactions, product catalogs, and dynamic content generation.
- Scalability: Dynamic websites can easily scale to accommodate growing traffic and evolving business needs by leveraging server-side technologies, load balancing, caching, and cloud infrastructure.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Dynamic websites are generally more complex to develop, deploy, and maintain compared to static websites due to server-side scripting, database integration, security considerations, and performance optimization.
- Resource Intensive: Dynamic websites require server-side processing for each user request, which can consume more server resources (CPU, memory, bandwidth) compared to serving static content, potentially leading to slower loading times and increased hosting costs.
- Security Risks: Dynamic websites are more susceptible to security vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and session hijacking due to the interaction with databases and user inputs, requiring robust security measures and regular updates to mitigate risks.
- Dependency on Server-Side Technologies: Dynamic websites rely on server-side scripting languages, frameworks, and databases, which may introduce dependencies and compatibility issues, making it challenging to migrate or upgrade the website infrastructure.
- Performance Concerns: Dynamic websites can experience performance bottlenecks under heavy traffic loads or complex processing requirements, necessitating optimization techniques such as caching, database indexing, and code optimization to improve responsiveness and scalability.
What are the difference between Static and Dynamic Website?

Static and dynamic websites differ in several key aspects:
- Content Generation:
- Static websites: Content is fixed and pre-generated, typically stored as HTML files. Each user receives the same content.
- Dynamic websites: Content is generated on-the-fly in response to user requests or interactions, often using server-side scripting and database queries. Content can be personalized and may vary for each user.
- Interactivity:
- Static websites: Limited interactivity, usually consisting of hyperlinks and basic navigation.
- Dynamic websites: Offer more interactivity with features like forms, user authentication, real-time updates, and user-generated content.
- Maintenance:
- Static websites: Generally simpler to maintain since content updates involve directly editing HTML files. However, scaling and managing large volumes of content can be challenging.
- Dynamic websites: Require more maintenance due to server-side scripting, database management, and ongoing updates to dynamic content and features. Content management systems (CMS) are commonly used to streamline maintenance tasks.
- Performance:
- Static websites: Tend to load faster since content is pre-generated and served directly from the web server without server-side processing.
- Dynamic websites: May have slower loading times due to server-side processing and database interactions. Performance optimization techniques such as caching and content delivery networks (CDNs) are often employed to mitigate this.
- Scalability:
- Static websites: Typically easier to scale for high traffic volumes since they don’t require server-side processing. Hosting static websites on CDNs can further enhance scalability.
- Dynamic websites: Require more resources to scale efficiently, especially for complex applications with heavy server-side processing and database queries. Load balancing, caching, and cloud hosting are commonly used to handle scalability challenges.
- Functionality:
- Static websites: Primarily suitable for showcasing information, portfolios, or blogs where content doesn’t change frequently.
- Dynamic websites: Offer a wider range of functionalities such as e-commerce, user authentication, content management, forums, social networking, and web applications with real-time updates and user interactions.